This article will be split into 2 main parts, this one will attempt to explain the creation of a neutron star and the second will be about what is inside of a neutrons star.
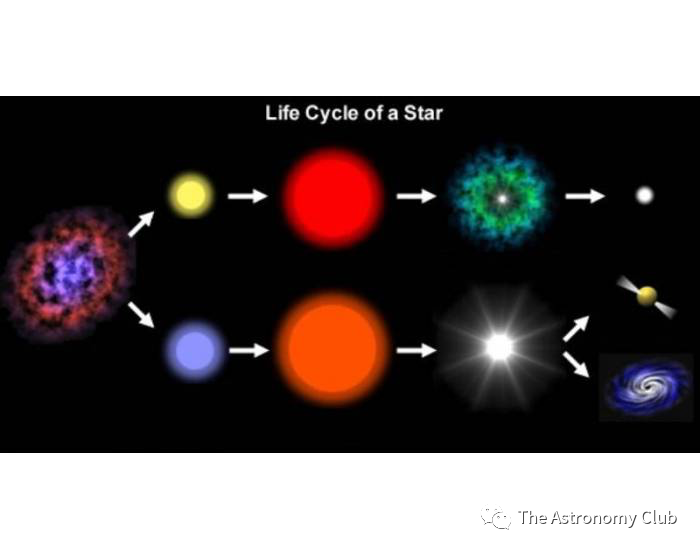
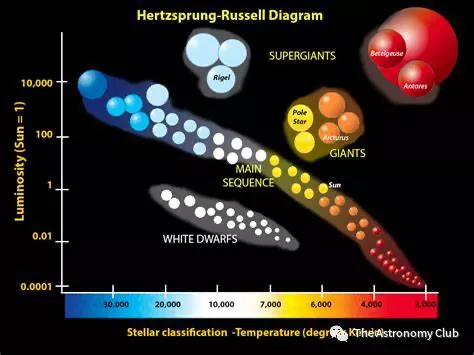
In order to understand how a neutron star is formed it requires a knowledge of the life cycles of a star. The life cycle of a star depends on the mass of that particular star. The majority of stars have the mass around the same as the sun called the main sequence, while much larger stars are called super giants and the smaller ones although rare are called dwarfs.
Hertzprung-Rusell Diagram (for types of masses of stars)
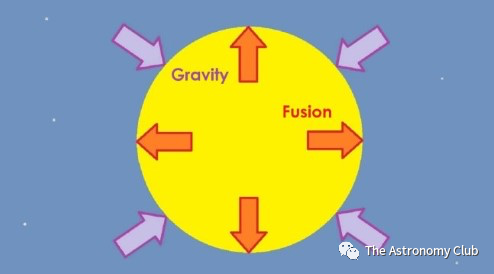
Main Sequence stars maintain balance through nuclear fusion, where they first fuse together Hydrogen to become Helium and so on, forming heavier metals that sink into the core of the star, while releasing massive amounts of violent energy outwards. The pressures of nuclear reactions balance out the gravity of the mass pushing inwards in a fragile balance called Hydrostatic Equilibrium. Over time, the star ages and more mass becomes at the core, the nuclear fusion becomes stronger and more rapid, becoming stronger than the gravitational force. This makes the star expand into what is known as a red giant. Then eventually there is not enough fuel/mass to perform nuclear fusion, and it explodes into a planetary nebula. The nebula is the nursery grounds for the birth of new stars, and in the place of the star, the white dwarf is formed. The white dwarf is a tiny but stable form, it burns a faint white light until finally disappearing into a black dwarf. Note that it takes so long to burn out a white dwarf that none exist currently because out universe is not old enough.
Hydrostatic equilibrium
Giant/Supergiant stars have a more rapid nuclear reaction rate, and so die a lot quicker and more violently. Instead of becoming a red giant, they become a red supergiant. Eventually the super giants become so unstable that the gravity far outpowers the fusion reaction since its mass is so large, and it collapses into a infinitely small point called a singularity. It implodes into a reaction called a Supernova, that is so bright that in a few seconds it can outshine entire galaxies. But depending out of the mass, two resulting objects may be formed. The first is the most famous: Black Holes. Black holes are created when a tipping point where the mass remains at the singularity and everything past the area of the event horizon is sucked into the point, even light is pulled in, which is why it is called a black hole. The second type is Neutron stars, these have weird internal structures and particle make up that will be covered in the next article. Sometimes they become pulsar where they spin with EM waves at extremely fast rate of around 3000 spins per second, with a high magnetized compact star. It has the density as the mass of Mount Everest in a single sugar cube, or 333000 times the mass of Earth at the size of New York, for perspective of how dense it is.
Life cycle of A star