
目 的
本研究的目的是评估硬膜外利多卡因联合美沙酮或吗啡用于接受卵巢子宫切除术的猫术后镇痛的有效性。
方 法
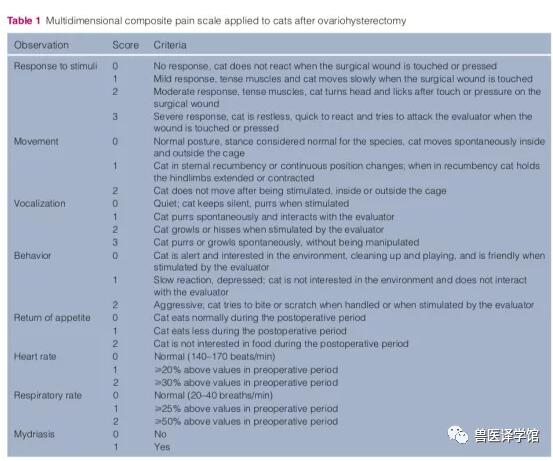
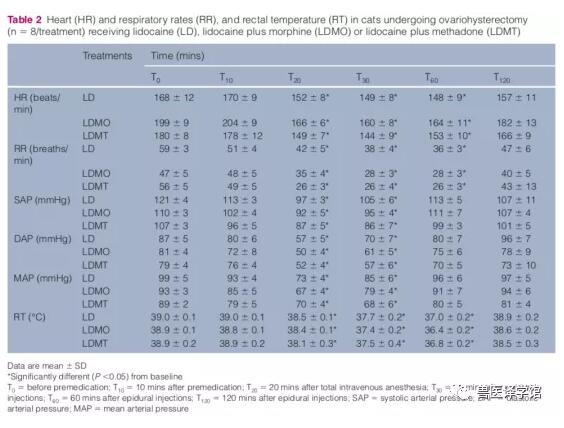
在全身麻醉下,24只接受卵巢子宫切除术的猫被随机分为三个治疗组,每组8只。治疗1包括2%利多卡因(4.0 mg/kg);治疗2包括利多卡因和美沙酮(分别为4.0 mg/kg和0.3 mg/kg);治疗3包括利多卡因和吗啡(分别为4.0 mg/kg和0.1 mg/kg)。所有猫均通过腰骶部途径以0.25 ml/kg的总体积注射所有药物。在麻醉和手术期间,每隔0、10分钟、20分钟、30分钟、60分钟和120分钟测量生理变量(呼吸和心率、动脉血压和直肠温度)。在猫从麻醉中恢复后,使用多维复合疼痛量表评估硬膜外麻醉后2、4、8、12、18和24小时的术后镇痛。
结 果
与单独接受利多卡因治疗的猫相比,同时接受利多卡因和美沙酮或利多卡因和吗啡治疗的猫首次止痛药的时间显著延长(P<0.05)。所有单独接受利多卡因治疗的猫在硬膜外注射后2小时内都需要止痛药。所有治疗均产生显著的心血管和呼吸变化,但在手术期间,这些变化在健康动物可接受的范围内。
结 论
在接受OHE的猫中,与单独使用利多卡因相比,腰骶部硬膜外注射美沙酮和吗啡加利多卡因可提供更长的术后镇痛持续时间。美沙酮和吗啡的不良反应没有差异。本研究中使用的两种联合阿片类药物,利多卡因加美沙酮和利多卡因加吗啡,在猫OHE后诱导更长时间的有效镇痛和首次抢救镇痛。出于这些原因,这些组合应被视为缓解此类手术后疼痛的镇痛技术
个人经验与感想
1.阿片受体(μ、κ和δ)高浓度存在于脊髓,主要在背角。阿片类物质激活这些受体可抑制C伤害性纤维释放P物质;然而,阿片类药物对A-δ抑制无效。A-δ纤维负责过急性(手术)疼痛,在整个手术过程中由于持续的刺激而被激活。局部麻醉剂对这些产生麻醉的纤维有效。局部麻醉药与阿片类药物联合使用具有优势,因为它可以减少硬膜外腔两种药物的剂量,并可能在预防手术疼痛传播方面产生协同作用。由于镇痛作用是通过脊髓背角的阿片受体进行的,因此通过硬膜外途径给药的阿片类药物不会干扰行走,也不会引起中枢神经系统的抑制。μ激动性阿片类药物可通过超极化运动神经元影响运动功能,但很少出现运动功能减弱。
2.上述的药物单独使用或联用优点很多,但不可忽略硬膜外给药的副作用,其中包括心率血压的降低、心律不齐、呼吸抑制、神经损伤、穿刺部位出血及感染的风险等。因此需要麻醉医生在选择使用硬膜外给药时,需注意穿刺部位的消毒、穿刺位点的确认及药物使用的剂量。
3.麻醉医生老生常谈的问题:利多卡因和猫。在本人的临床操作过程当中,目前未遇到猫使用利多卡因后出现心脏毒性或CNS抑制/毒性的情况。在操作时需确定穿刺未见明显出血后方可推注麻醉药物。
4.若仅需后躯进行镇痛的情况下,可使用骶尾骨硬膜外麻醉的技术,
同时需要注意无菌操作。
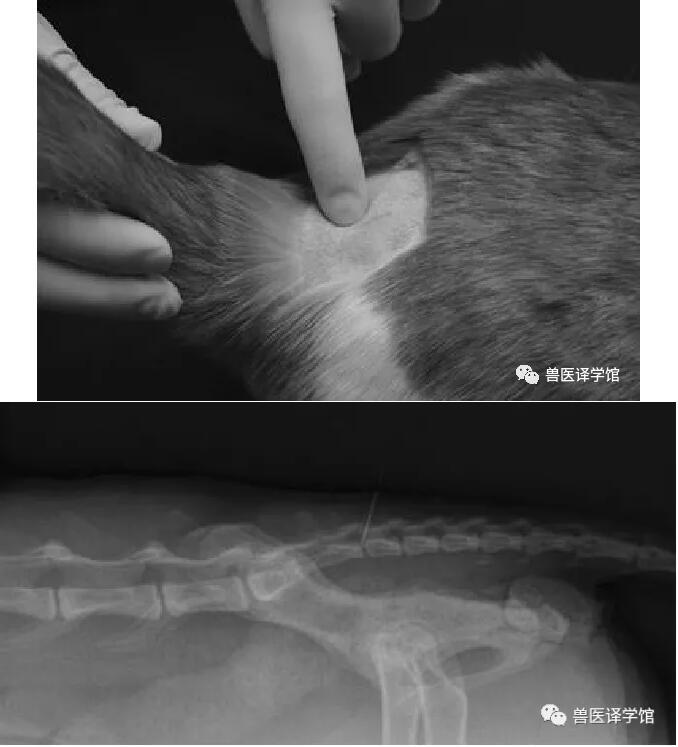
5.麻醉医生应努力掌握硬膜外麻醉及其他局部麻醉的技术,尽可能降低犬猫围手术期的疼痛。
Postoperative pain control in cats: clinical trials with pre-emptive lidocaine epidural co-administered with morphine or methadoneObjectives The aim of the study was to evaluate the effectiveness of epidural lidocaine in combination with either methadone or morphine for postoperative analgesia in cats undergoing ovariohysterectomy.Methods Under general anesthesia, 24 cats that underwent ovariohysterectomy were randomly allocated into three treatment groups of eight each. Treatment 1 included 2% lidocaine (4.0 mg/kg); treatment 2 included lidocaine and methadone (4.0 mg/kg and 0.3 mg/kg, respectively); and treatment 3 included lidocaine and morphine (4.0 mg/kg and 0.1 mg/kg, respectively). All drugs were injected in a total volume of 0.25 ml/kg via the lumbosacral route in all cats. During the anesthetic and surgical periods, the physiologic variables (respiratory and heart rate, arterial blood pressure and rectal temperature) were measured at intervals of time zero, 10 mins, 20 mins, 30 mins, 60 mins and 120 mins. After cats had recovered from anesthesia, a multidimensional composite pain scale was used to assess postoperative analgesia 2, 4, 8, 12, 18 and 24 h after epidural.Results The time to first rescue analgesic was significantly (P <0.05) prolonged in cats that received both lidocaine and methadone or lidocaine and morphine treatments compared with those that received lidocaine treatment alone. All cats that received lidocaine treatment alone required rescue analgesic within 2 h of epidural injections. All treatments produced significant cardiovascular and respiratory changes but they were within an acceptable range for healthy animals during the surgical period.Conclusions and relevance The two combinations administered via epidural allowed ovariohysterectomy with sufficient analgesia in cats, and both induced prolonged postoperative analgesia.



