
图1 身高(PC1和PC2)或性别(PC4)对膝关节骨形状和软骨厚度耦合变化的影响[1]
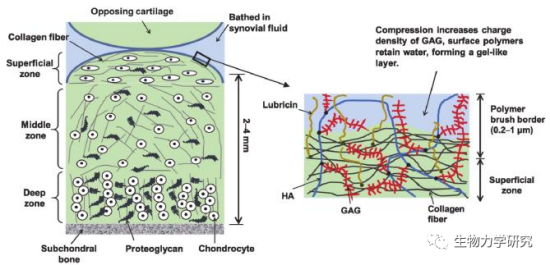
图2 软骨结构和表面细节示意图[2]
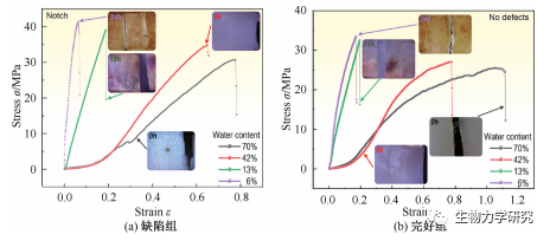
图3 含水量不同软骨拉伸应力-应变关系[4]

图4 膝关节软骨切片方法和压痕位置[6]
2 关节软骨力学生物学研究
2.1软骨力学生物学研究的加载装置
2.2 体外力学生物学研究

图5 体外压缩载荷下促进组织再生的成熟人工软骨培养及关节软骨缺损修复过程示意图[25]
注:a、b、c分别为接种软骨细胞进入支架、在体外压缩载荷下构建成熟的人工软骨、成熟软骨细胞/支架的植入缺损示意图。
2.3 在体力学生物学研究
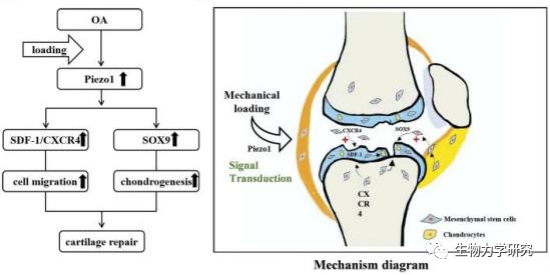
图6 力学传导机制图[22]
参考文献 [1] SCHNEIDER MT, ROOKS N, BESIER T. Cartilage thickness and bone shape variations as a function of sex, height, body mass, and age in young adult knees [J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12: 11707. [2] LIAO J, SMITH DW, MIRAMINI S, et al. Investigation of role of cartilage surface polymer brush border in lubrication of biological joints [J]. Friction, 2022,doi:10.1007/s40544-020-0468-y. [3] HUA X, SHU L, LI J. Multiscale modelling for investigating the long-term time-dependent biphasic behaviour of the articular cartilage in the natural hip joint [J]. Biomech Model Mechanobiol, 2022, 21: 1145-1155. [4] LIU JZ, XU ST, MA ZC, et al. Water loss and defects dependent strength and ductility of articular cartilage [J]. J Mater Res Technol, 2022, 21: 1714-1723. [5] MOO EK, EBRAHIMI M, SIBOLE SC, et al. The intrinsic quality of proteoglycans, but not collagen fibres, degrades in osteoarthritic cartilage [J]. Acta Biomater, 2022, 153: 178-189. [6] MA ZC, HUANG B, LIU DN, et al. Full domain surface distributions of micromechanical properties of articular cartilage structure obtained through indentation array [J]. J Mater Res Technol, 2022, 17: 2259-2266. [7] SI Y, TAN Y, GAO L, et al. Mechanical properties of cracked articular cartilage under uniaxial creep and cyclic tensile loading [J]. J Biomech, 2022, 134: 110988. [8] ECKSTEIN KN, THOMAS SM, SCOTT AK, et al. The heterogeneous mechanical properties of adolescent growth plate cartilage: A study in rabbit [J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2022, 128: 105102. [9] 宫赫,张萌,邹姗姗.肌骨系统生物力学建模2021年研究进展[J].医用生物力学,2022,37(1): 18-26 GONG H, ZHANG M, ZOU S. Research advances in musculoskeletal biomechanical modeling in 2021 [J]. J Med Biomech, 2022, 37(1): 18-26. [10] LOGERSTEDT DS, EBERT JR, MACLEOD TD, et al. Effects of and response to mechanical loading on the knee [J]. Sports Med, 2022, 52(2): 201-235. [11] WANG XY, GUO JQ, TIAN Q. A forward-inverse dynamics modeling framework for human musculoskeletal multibody system [J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2022, 38(11): 522140-1. [12] XIONG B, YANG P, LIN T, et al. Changes in hip joint contact stress during a gait cycle based on the individualized modeling method of "gait-musculoskeletal system-finite element" [J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2022, 17: 267. [13] SHIH KS, HSU CC. Three-dimensional musculoskeletal model of the lower extremity: Integration of gait analysis data with finite element analysis [J]. J Med Biol Eng, 2022, 42: 436-444. [14] IVO R, RODRIGUES DSM, FILIPE M, et al. On the modeling of biomechanical systems for human movement analysis: A narrative review [J]. Arch Comput Methods Eng, 2022, 29: 4915-4958. [15] WU CC, YE LM, LI XF, et al. Sequential damage assessment of the posterolateral complex of the knee joint: A finite element study [J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2022, 17(1): 185. [16] MA P, MUHEREMU A, ZHANG S, et al. Biomechanical effects of fixed-bearing femoral prostheses with different coronal positions in medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2022, 17(1): 150. [17] GAO L, LIU G, TAN Y, et al. Creep-recovery behaviors of articular cartilage under uniaxial and biaxial tensile loadings [J].Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023, 10: 1085062. [18] SANTOS S, NEU CP, GRADY JJ, et al. Genipin does not reduce the initiation or propagation of microcracks in collagen networks of cartilage [J]. Osteoarthr Cartil Open, 2022, 4(1): 100233. [19] ORAVA H, HUANG L, OJANEN SP, et al. Changes in subchondral bone structure and mechanical properties do not substantially affect cartilage mechanical responses - A finite element study [J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2022, 128: 105129. [20] WOOK HJ, DIPUL C, GUEBUM H, et al. Effects of solvent osmolarity and viscosity on cartilage energy dissipation under high-frequency loading [J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2022, 126: 105014. [21] HUI MINGALONE CK, NEHME CR, CHEN Y, et al. A novel whole "Joint-in-Motion" device reveals a permissive effect of high glucose levels and mechanical stress on joint destruction [J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2022.10.018. [22] LI J, WANG X, LI X, et al. Mechanical loading promotes the migration of endogenous stem cells and chondrogenic differentiation in a mouse model of osteoarthritis [J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2022, doi: 10.1007/s00223-022-01052-1. [23] ONAL S, ALKAISI MM, NOCK V. Microdevice-based mechanical compression on living cells [J]. iScience, 2022, 25(12): 105518. [24] GU MJ, FAN SN, ZHOU GD, et al. Effects of dynamic mechanical stimulations on the regeneration of in vitro and in vivo cartilage tissue based on silk fibroin scaffold [J].Compos Part B-Eng, 2022, 235: 109764. [25] LIN XL, GAO LL, LI K, et al. Construction and tissue regeneration evaluation for mature chondrocyte/scaffold complex under optimal compression loading [J]. Mater Design, 2022, 224: 111276. [26] SANI M, HOSSEINIE R, LATIFI M, et al. Engineered artificial articular cartilage made of decellularized extracellular matrix by mechanical and IGF-1 stimulation [J]. Biomater Adv, 2022, 139: 213019. [27] VINOD E, PADMAJA K, RAMASAMY B, et al. Systematic review of articular cartilage derived chondroprogenitors for cartilage repair in animal models [J]. J Orthop, 2023, 35: 43-53. [28] CAINE D, MEYERS R, NGUYEN J, et al. Primary periphyseal stress injuries in young athletes: A systematic review [J]. Sports Med, 2022, 52(4): 741-772. [29] ALONSO G, YAWNY A, BERTOLINO G. How do bones grow? A mathematical description of the mechanobiological behavior of the epiphyseal plate [J]. Biomech Model Mechanobiol, 2022, 21(5): 1585-1601. [30] ESDAILLE CJ, UDE CC, LAURENCIN CT. Regenerative engineering animal models for knee osteoarthritis [J]. Regen Eng Transl Med, 2022, 8: 284-297. [31] CHILBULE SK, RAJAGOPAL K, WALTER N, et al. Role of WNT agonists, BMP and VEGF antagonists in rescuing osteoarthritic knee cartilage in a rat model [J]. Indian J Orthop, 2022, 56(1): 24-33. [32] ZHOU L, GUO P, D'ESTE M, et al. Functionalized hydrogels for articular cartilage tissue engineering [J]. Engineering, 2022, 13: 71-90. [33] YANG Y, ZHENG W, TAN W, et al. Injectable MMP1-sensitive microspheres with spatiotemporally controlled exosome release promote neovascularized bone healing [J]. Acta Biomater, 2022, 157: 321-336. [34] CAO D,DING J.Recent advances in regenerative biomaterials [J].Regen Biomater, 2022, 9: rbac098 [35] ZHANG Y, LI S, JIN P, et al. Dual functions of microRNA-17 in maintaining cartilage homeostasis and protection against osteoarthritis [J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 2447. [36] 卢启贵,谢平金,罗臻, 等. MicroRNA-20b-5p对早期膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨和软骨下骨血管新生的影响 [J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(29): 4658-4665. 作者简介 张春秋 张春秋,教授,博士生导师,天津市先进机电系统设计与智能控制重点实验室主任,现工作于天津理工大学机械工程学院。中国生物力学专业委员会委员,天津体视学会副理事长,天津生物力学专业委员会副主任委员,天津力学学会理事;2017年天津市高校学科领军人才;2013年中青年骨干创新人才;杜庆华力学与工程奖(2016)。 主要研究方向是仿生设计理论与智能制造,包括生物力学和结构强度分析。生物力学研究包括骨、软骨力学性能与力学生物学;组织工程生物反应器;关节3D打印假体植入物的研制。结构强度分析包括机械结构的数值仿真及应力、应变的实验测试。